AI-Powered Seismic Interpretation in
the Western Gulf of Mexico
Introduction
A study was conducted in 2024 to gauge the effectiveness of Interpretation.AI in the Western Gulf of Mexico. Multiple seismic facies were interpreted in a fault prone area. This white paper presents an AI-driven approach to seismic facies interpretation that significantly reduces the time required for analysis while maintaining high accuracy.
Background
The study utilizes a vintage 3D seismic provided courtesy of Viridien and Seitel. The survey contains 976 time-migrated seismic lines. Eleven facies were interpreted over the survey by a human interpreter over approximately 8 days. A small subset of the labeled lines were then used to train the model and an AI-assisted interpretation was then created and compared to the human interpretation of the seismic volume. By leveraging AI-assisted interpretation, we demonstrate substantial improvements in efficiency without compromising accuracy.
AI Training and Methodology
Data Preparation and Labeling
- A small subset of labeled seismic data (.26%) was used to train the AI.
- The labeling and training process was completed in one day.
- The AI results were then compared to the human interpretation in areas where no labeled data was provided.
AI Model Performance
The AI model was evaluated using two key metrics:
- Global Intersection over Union (IoU):
Measures overall accuracy in a seismic volume interpretation compared to human interpretation. It is evaluated on a pixel by pixel level. If the AI interprets the facies exactly like the human interpreter, the pixel value is 1. If not, the value is 0. The average for all pixels then determines the Global IoU.
- Mean IoU:
Same methodology as before but run on each individual facies. The average of the facies results together determines the Mean IoU.
With 0.26% labeled data, the AI model achieved:
RGB |
Class |
IoU |
|---|---|---|
| H0 | 0.992 | |
| H1 | 0.972 | |
| H2 | 0.924 | |
| H3 | 0.857 | |
| H4 | 0.947 | |
| H5 | 0.851 | |
| H6 | 0.952 | |
| H7 | 0.970 | |
| H8 | 0.958 | |
| H9 | 0.887 | |
| Basement | 0.993 |
- Global IoU: 0.967
- Mean IoU: 0.935
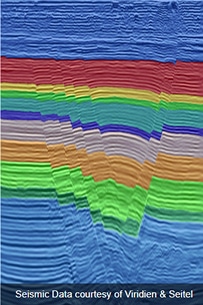
Interpreter
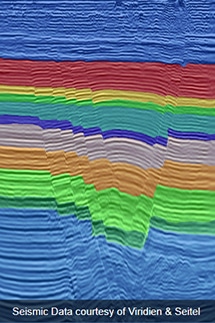
AI
Conclusion
AI-driven seismic interpretation has demonstrated significant advantages in efficiency and accuracy. The reduction in interpretation time from 2 months to 2 days is a paradigm shift in geophysical data analysis in situations where turnaround time is critical. Future work includes an expansion to include AI-assisted fault interpretation and expansion to other geological basins.
